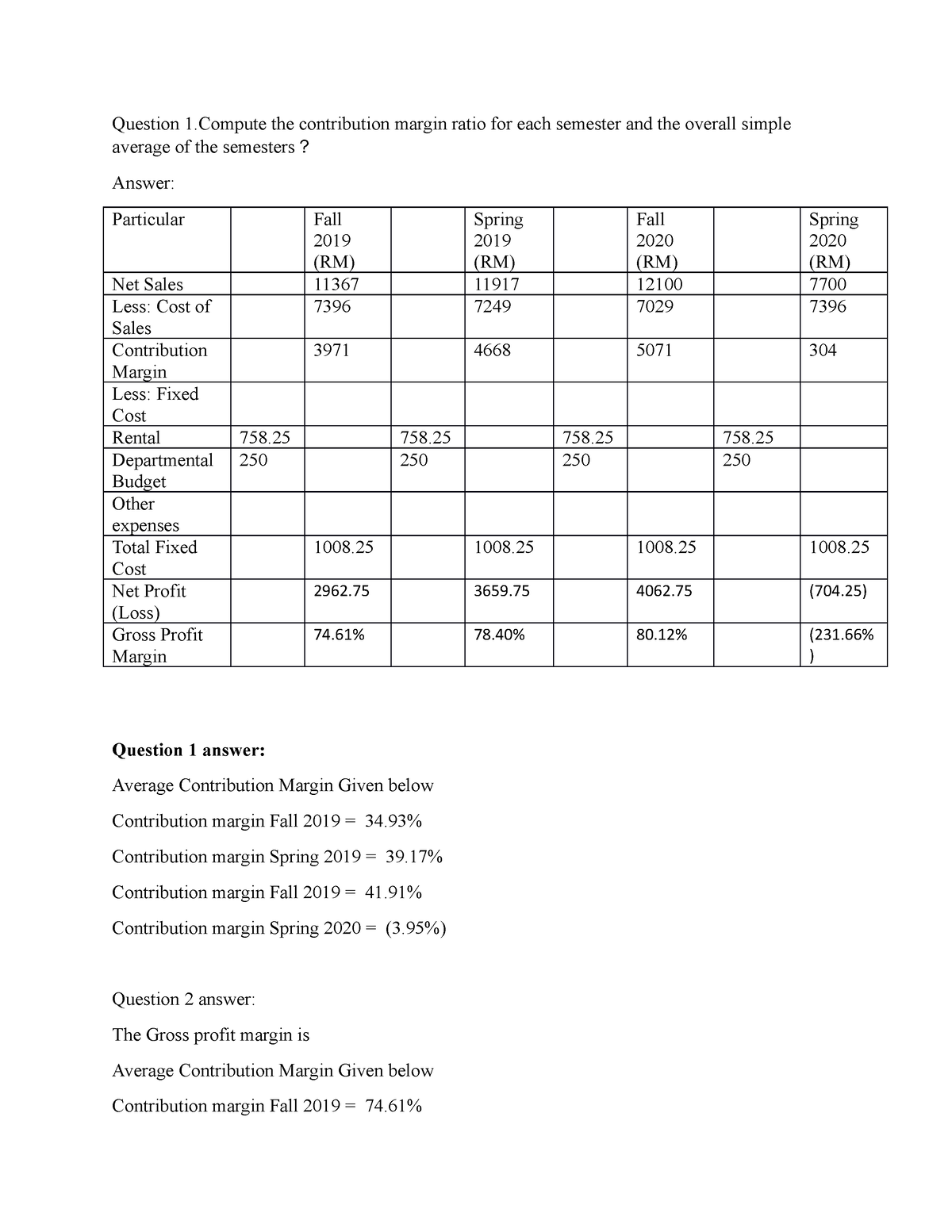
Whether you sell millions of your products or 10s of your products, these expenses remain the same. You can even calculate the contribution margin ratio, which expresses the contribution margin as a percentage of your revenue. In short, profit margin gives you a general idea of how well a business is doing, while contribution margin helps you pinpoint which products are the most profitable. In May, \(750\) of the Blue Jay models were sold as shown on the contribution margin income statement. When comparing the two statements, take note of what changed and what remained the same from April to May. By analyzing the contribution margin, businesses can identify which costs are impacting their profitability the most and strategize accordingly to reduce these expenses.
Why are contribution margins and contribution margin ratios important to you?
The companies that operate near peak operating efficiency are far more likely to obtain an economic moat, contributing toward the long-term generation of sustainable profits. Aside from the uses listed above, the contribution margin’s importance also lies in the fact that it is one of the building blocks of break-even analysis. With that all being said, it is quite obvious why it is worth learning the contribution margin formula. There is no definitive answer to this question, as it will vary depending on the specific business and its operating costs.
Fixed Cost vs. Variable Cost
Contribution Margin Ratio (CMR) is a measurement tool found on a company’s income statement and its balance sheet. The CMR indicates the amount of income a company has left over after all its expenses have been paid. This tool is essential in helping to determine how much money is available for distribution to owners as dividends and how much money is available for reinvestment in the company. To figure this out, divide the cost of goods sold for each product by its selling price. For example, if a product costs you $10 to make and you charge $12, your contribution margin is 25%. Other financial metrics related to the Contribution Margin Ratio include the gross margin ratio, operating margin ratio, and net profit margin ratio.
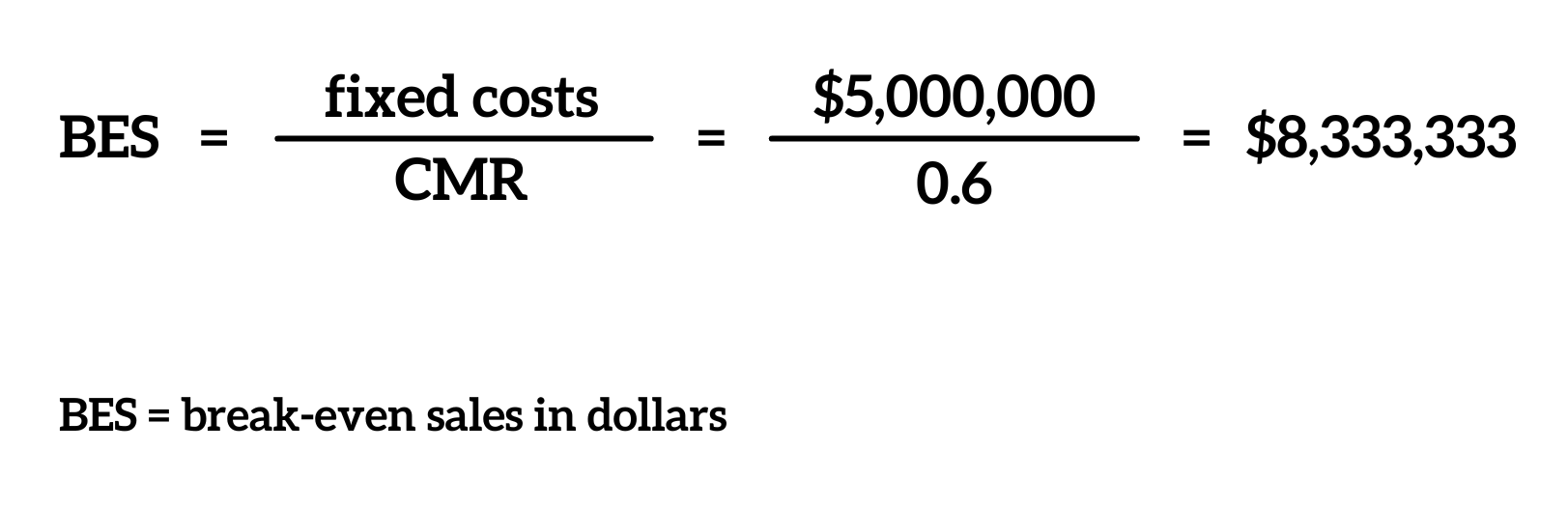
Business Class
In our example, if the students sold \(100\) shirts, assuming an individual variable cost per shirt of \(\$10\), the total variable costs would be \(\$1,000\) (\(100 × \$10\)). If they sold \(250\) shirts, again assuming an individual variable cost per shirt of \(\$10\), then the total variable costs would \(\$2,500 (250 × \$10)\). That said, most businesses operate with contribution margin ratios well below 100%. The Contribution Margin Calculator is a powerful tool that simplifies this critical calculation. Designed with business owners in mind, it takes into account various factors such as sales revenue, variable costs, and the number of units sold to provide a clear picture of your contribution margin. A negative contribution margin indicates that variable costs exceed sales revenue, which means you’re losing money on each unit sold.
- Other reasons include being a leader in the use of innovation and improving efficiencies.
- By knowing the exact contribution of each product to the overall profit, businesses can make informed decisions about pricing adjustments.
- The overarching objective of calculating the contribution margin is to figure out how to improve operating efficiency by lowering each product’s variable costs, which collectively contributes to higher profitability.
- The resulting ratio compares the contribution margin per unit to the selling price of each unit to understand the specific costs of a particular product.
- The contribution margin ratio, often abbreviated as “CM ratio”, expresses the residual profits generated from each unit of product sold, once all variable costs are subtracted from product revenue.
Using the contribution margin formulas – example
Variable expenses can be compared year over year to establish a trend and show how profits are affected. In the next part, we must calculate the variable cost per unit, which we’ll determine by dividing the total number of products sold by the total variable costs incurred. The contribution margin ratio, often abbreviated as “CM ratio”, expresses the residual profits generated from each unit of product sold, once all variable costs are subtracted from product revenue. The contribution margin is the leftover revenue after variable costs have been covered and it is used to contribute to fixed costs.
How does the contribution margin affect profit?
And to understand each of the steps, let’s consider the above-mentioned Dobson example. The gross sales revenue refers to the total amount your business realizes from the sale of goods or components of the master budget services. That is it does not include any deductions like sales return and allowances. Thus, the total manufacturing cost for producing 1000 packets of bread comes out to be as follows.
Such fixed costs are not considered in the contribution margin calculations. It provides one way to show the profit potential of a particular product offered by a company and shows the portion of sales that helps to cover the company’s fixed costs. Any remaining revenue left after covering fixed costs is the profit generated.
This situation needs urgent attention to either reduce variable costs or increase sales revenue. When a firm decides which products to offer or which markets to penetrate, it should examine each product’s contribution margins to determine if it will contribute enough profit to cover its fixed costs. If not, the firm cannot produce that product or not enter that market segment. The contribution margin ratio (CMR) is a financial ratio that measures the proportion of revenue available to cover fixed costs and contribute to profit. Similarly, we can then calculate the variable cost per unit by dividing the total variable costs by the number of products sold.
One reason might be to meet company goals, such as gaining market share. Other reasons include being a leader in the use of innovation and improving efficiencies. If a company uses the latest technology, such as online ordering and delivery, this may help the company attract a new type of customer or create loyalty with longstanding customers.
This ratio is particularly useful in evaluating the profitability of different products or services within your business. To use the calculator, you’ll input your total sales revenue, variable costs per unit, and the total number of units sold. The calculator then processes these inputs to deliver not just the contribution margin but also the contribution margin ratio and the total profit generated. Using this formula, the contribution margin can be calculated for total revenue or for revenue per unit. For instance, if you sell a product for $100 and the unit variable cost is $40, then using the formula, the unit contribution margin for your product is $60 ($100-$40).
